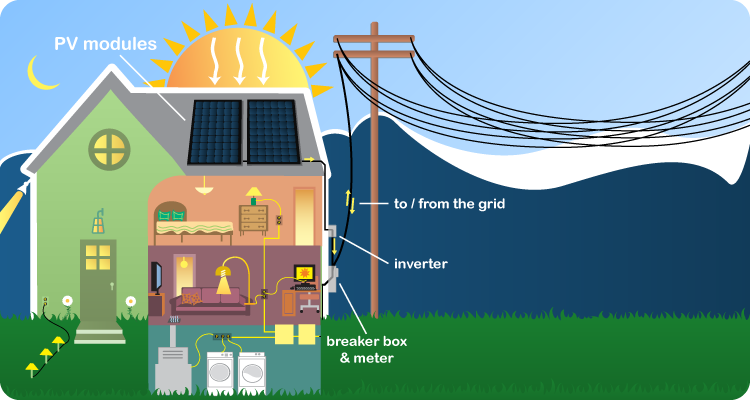
How Solar Works
Solar Energy Terminology is Relatively New
Take a Moment to Understand the Terms & Issues
AC – Alternating current is a wave form of electricity varying from positive to negative at 60 times per second (60Hz). This is the measurement used for all your household electrical needs and is the measurement used on your electricity bills.
DC – Direct Current is the form of electricty generated by solar panels and it needs to converted to AC to be useable in the home. This conversion is done by means of an inverter. Make sure you understand the difference between AC & DC when looking at quotations for solar systems. Systems quoted in DC appear larger than an identical system quoted in AC.
Electric panel – The electric panel is the main service to your home or business. It is where the power is supplied to the building from the utility company and where you draw power for consumption in the building. The electric panel also includes the meter which records the power consumption.
Expected Performance Based Buy Down (EPBB) – EPBB is a type of incentive structure offered as part of the California Solar Initiative (CSI). The EPBB is used for systems smaller than 50 kW, which are usually installed on homes and small commercial applications. This structure offers an up-front incentive based on the system’s expected usage. Incentives are calculated on a sliding scale and decline as more solar reservations are made, so time is of the essence.
Grid-tied– Grid-tied systems operate in parallel with and are connected to the electric utility grid. Most residential PV systems are grid-tied, which allows you to reduce or even eliminate your monthly electricity bills without having to change your lifestyle.
Ground Mount – There are various methods of installing a solar system of which ground mounted systems is one. Ground mounted systems are not attached to a home or building, but rather installed using a solar specific structure that supports the solar panels. Ground mounts are ideal for customers with inadequate roof space.
Inverter – An inverter is a device that converts DC power from the solar panels, to AC power that can be used in your home and business. The inverter is wired directly into the main electric panel, when more power is being generated than consumed, the meter runs backwards.
Kilowatt (kW) – A measure of power equivalent to 1,000 watts or the power required to run ten 100 watt light bulbs in any instant.
Kilowatt Hour – (kWh – A common unit of electrical consumption measured by the total energy created by one kilowatt in one hour. A 100 watt light bulb burning for 10 hours uses one kilowatt hour. To determine the size of the solar system you’ll need, we’ll look at your electricity bills over time to see how many kWhs you typically use and will need in the future.
Megawatt – A measure of power equivalent to one million watts.
NABCEP – The North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners is a national program that awards professional certification to photovoltaic installers. NABCEP’s high standards are designed to protect customers and enhance the profession.
Net Metering – A policy under which a solar system owner can generate electricity during daylight hours and consume grid power over night and settle the utility bill either monthly or annually for the net amount consumed. There is no payment from the utility for excess generation over the net metering period so Solar Plus will size your system to meet your specific needs.
Performance Based Incentive (PBI) – PBI is a type of incentive structure offered as part of the California Solar Initiative (CSI). The PBI structure is typically used for systems greater than 50 kWh and offers a flat rate per kWh. Incentives decline as more solar reservations are made, so now is the time to go solar.
Photon – A photon is a particle of energy contained in sunlight, the photons are the carriers of the energy that is converted to electricity by the solar cells in the solar panels.
Photovoltaic – Photovoltaics, or PV as you’ll often see it, is a solar energy technology that uses unique properties of semiconductors to directly convert solar radiation into energy. When PV cells, or solar cells, are combined into larger systems called modules, they produce energy with no moving parts, noise, or pollution.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) – PPAs are long-term contracts between the customer and the developer where the developer retains ownership of the system and sells the electricity to the customer at a specified rate for a specified amount of time. Essentially, the customer leases the solar system from the developer. PPAs have been standard throughout the power industry but are relatively new to the solar industry.
Roof Mount – The most common installation technique for solar, in which the solar system is attached to the roof of your home or building.
Solar Panel – A group of solar PV cells combined into a larger system to produce electrical power.
Utility Grid – The utility grid is the distribution system used by the power companies to transmit electricity from the generating facilities to the consumers. These are typically overhead wires from the small poles outside our houses to the large tower structures carrying power over long distances. Its purpose is to create a power-sharing system, directing power to where it is needed.